“Too little land, too many people” – it’s a common phrase Hongkongers use to describe their city of 7 million people. With a mountainous terrain and a rapidly increasing population, the struggle to find suitable land to build homes, offices and infrastructure has been a constant problem since the former British colony was transformed from a sleepy fishing village into a bustling metropolis.
As one of the most crowded cities in the world, the city has turned to a construction method that has been practiced throughout human history – land reclamation.
Hong Kong is just one of many examples where land reclamation contributed to growth and development. Large patches of land in Macau and Singapore, for example, are also created through land reclamation.
Dredge and Drain
To create new land in the middle of the ocean, one of the first steps is to build a foundation that’s strong and stable enough to support the weight everything else that goes on top.
Dredging the seabed to remove soft soil and draining water from the seafloor are two common ways to consolidate the foundation. But in locations where the seabed contains significant amount of contaminants, both methods can cause toxic substances to be released and damage marine ecology. Not only will this affect the water quality and marine life, but the contaminants could also enter the food chain and impact on public health.
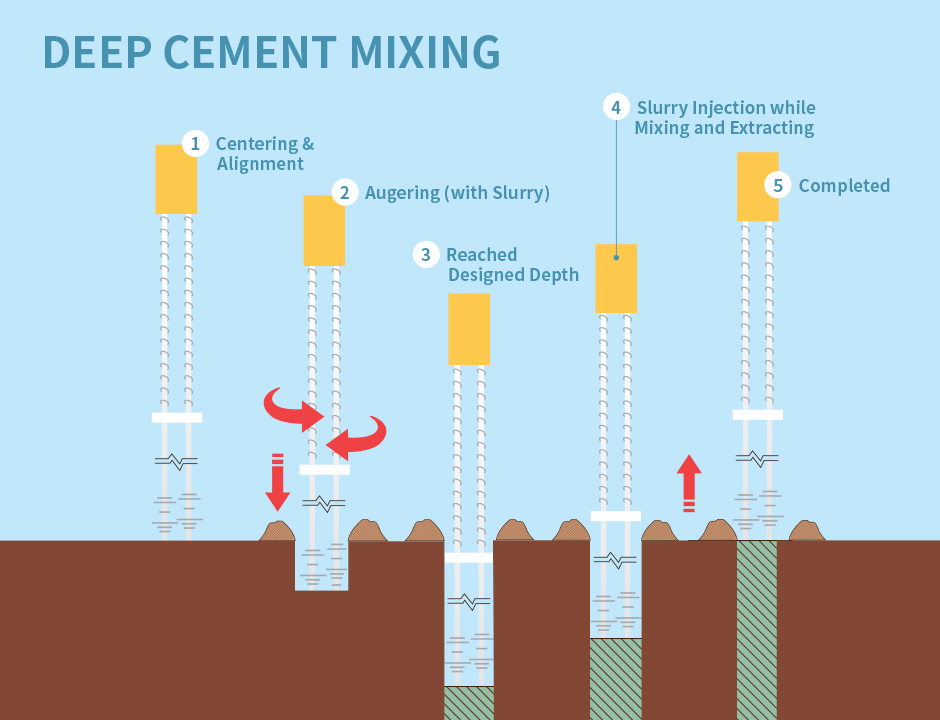
Deep Cement Mixing
How to improve the strength of the seabed without disturbing marine ecology in the land reclamation process? That’s the question which led engineers in Japan to develop an innovative ground consolidation method – Deep Cement Mixing or DCM.
The process begins by using an auger to drill narrow holes into the seabed. Once the machine reaches the desired depth, a binder material, most commonly cement, is injected to fill the space and mix with the soft mud. Once the cement is hardened, it forms a column embedded in the seabed. This process is repeated multiple times across the area selected for reclamation, creating large groups of columns that significantly increases the load bearing capacity of the seabed.
First tested in 1970s, the use of DCM in land reclamation was initially limited to Japan and Scandinavia. But by the 1980s, the method has gained widespread popularity.
DCM in Action
Samsung C&T is one of the world’s leading experts in soil consolidation and DCM is a key method the company employs to ensure its projects are effective and sustainable.
One of the company’s most notable DCM projects is the expansion of Hong Kong International Airport into a Three Runway System. Located north of the airport, consolidation of the soil at the 650 hectares site began in August 2016. Since 40% of the area consists of contaminated mud pits that were generated from dredging in other areas of the city, DCM was favored to limit the potential damage to the environment.
To further prevent toxic substances from being released, Samsung C&T engineers placed a two-meter-thick sand blanket on top of large sheets of geotextile on the seabed before drilling. Working like a filter, the projective layer removes any mud that sticks on the drills when they are lifted.
More recently, Samsung C&T began works on the extension of Tung Chung New Town in Hong Kong in January this year. To help tackle housing shortage in the city, the company will adopt DCM to create 134 hectares of reclaimed land in the northern part of Lantau Island. Expected to be completed by July 2024, the new land will be used to house over 200,000 residents.
Not only will the use of DCM ensure the strength of Hong Kong’s valuable marine life, both projects will also bring new employment opportunities and provide room for the city’s economy to grow.
A Solid Future
The demand for new land will grow as urban centers around the world become more populated. DCM will provide the foundation for meeting the needs of city-dwellers, while ensuring that urbanization can be sustainable.