Increasing urbanization in our modern developed world shows no signs of stopping. This brings into sharper relief the need for greater sustainability and resource efficiency, and we will need to learn how to live better and smarter together in larger cities while enjoying a good quality of life. The concept of a “smart city” is receiving attention as one of the ways to achieve this. Futurist Bernard Marr, writing in Forbes magazine in July this year, explains that “a smart city is one that leverages technology to increase efficiencies and improve the quality of services and life for its residents […] The idea is to use data and technology to make everyday life easier and better for the people who live and work in the city, while maximizing the use of resources.”
A world full of smart cities
Since 2014, the IESE business school at the University of Navarra in Barcelona has researched cities around the world (this year 174 in 80 countries) and compiles them into its Cities in Motion (CIMI) index. It ranks how smart cities are based on various dimensions: human capital, governance, urban planning, mobility and transportation, technology, environment, and others.
In 2020, for the second year in a row, London and New York ranked first and second, respectively. London ranked first in the human capital and international projection dimensions, second in governance and urban planning, and in the top 10 for mobility and transportation, as well as technology. New York ranked first in the categories of economy, mobility and transportation, and urban planning. It is also working hard to reduce waste and pollution in the coming decades.
In Korea, too, governments want to see smart cities lead the way to the future. Korea’s history of promoting such projects (previously known as “ubiquitous cities”) began in March 2008. The plan was to improve living standards and contribute toward balanced national growth through the efficient building and management of cities that had the necessary technological infrastructure built into them from the beginning.
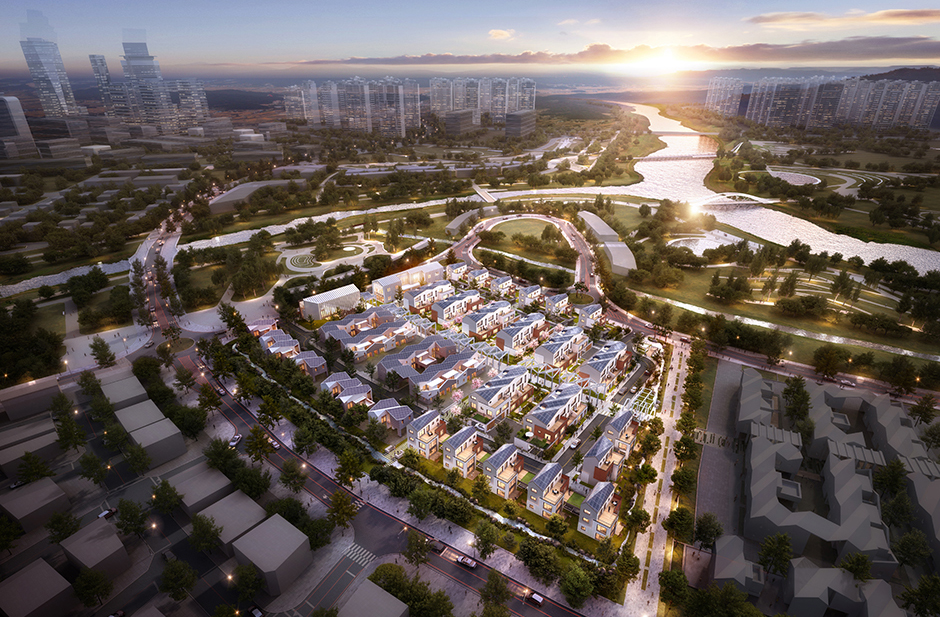
There are currently two pilot smart city projects in Korea: Busan Eco Delta City (EDC) and Sejong 5-1 Living Area. The Busan Eco Delta City project was inaugurated in November 2019 and is a jointly run by Busan City, K-Water, and Busan Metropolitan Corporation. It will see the development of 11.77 square kilometers of land in the Gangseo district of Busan into a waterfront eco city, a global cultural city, and a future logistics & service city. The Sejong project, located in the new administrative city south of Seoul, is for a community of 8,000 households and kicked off in July this year.
At Busan EDC, it takes a Smart Village
Samsung C&T Engineering & Construction Group has joined the project of building Korea’s smart city at an early stage, in winning an order for a “smart village” development project located in Busan EDC. Started in September 2020, it is slated for completion in December 2021, just 15 months later. The smart village will comprise 37 three-story houses and a community center.
Samsung C&T will employ eco-friendly technologies to reduce energy loss and achieve energy independence. For example, energy loss will be minimized by reducing outward facing surfaces, installing high-efficiency windows, and external electric blinds. Greenhouse gas emissions will be reduced by utilizing renewable or eco-friendly forms of energy such as solar, hydrothermal, and geothermal, and by transmitting the excess energy to energy storage systems in order to consume it at night.
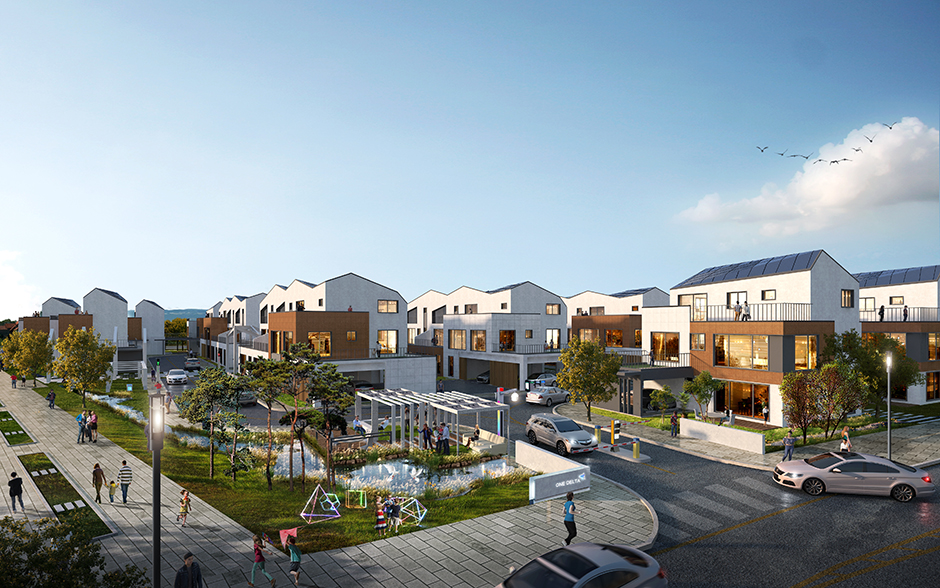
To create a customized residential environment, smart home technologies will be applied to all the dwellings. Samsung C&T’s has developed an “A.IoT” platform, which combines artificial intelligence with the Internet of Things. This platform will be used in Busan EDC to increase connectivity between systems and devices in the homes. Also, the residential data collected by the platform will be linked with external services such as healthcare, home security services, and energy saving. Furthermore, intelligent video surveillance systems, smart parking controls, and smart crosswalks will be installed in the public spaces of the village to make life more convenient.
Of course, a village is not just about the houses but also the public spacing in between. At Busan EDC, Samsung C&T will create eco-friendly and human-centered landscaping facilities by installing shared yards called “smart play yards” and walkways for pedestrians called “greenways”, connecting each house with private gardens and public walkways to turn spaces into communication channels between neighbors. Green spaces in the Smart Village will further be linked to a waterfront park, and species of plants and bushes will be planted that help lower fine dust levels and beautify the landscape each season. The tops of parking lots will be made into terraces to provide elevated outdoor spaces where residents can enjoy fresh air.
The 37 residences will share common spaces and facilities, which will help to foster a sense of community, for instance smart offices, sports facilities, unmanned convenience stores, delivery facilities, robot cafes, and community conference rooms.
The Smart Village development project in Busan EDC will be a very meaningful opportunity for Samsung C&T to be involved in the establishment of technology and infrastructure for building the smart city of the future. We look forward to the smart and sustainable future that Samsung C&T will help to construct.