Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are a flexible and efficient alternative to larger nuclear plants. They offer benefits like lower capital investment, improved safety features, and grid stability. Samsung C&T is becoming a key player in the global SMR market with the recent announcement of a collaborative project in Romania.
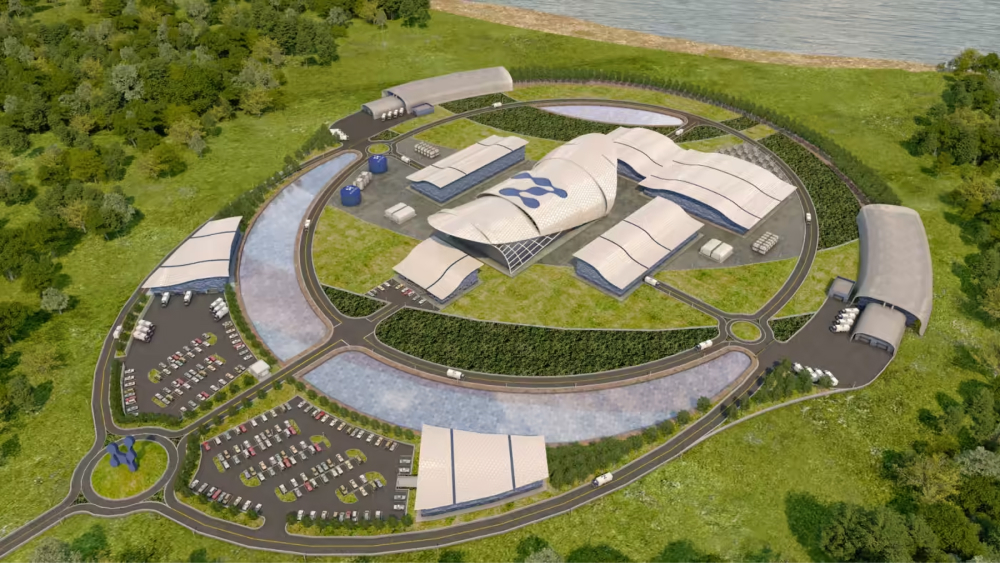

Samsung C&T’s Engineering and Construction (E&C) Group is entering the Small Modular Reactor (SMR) market with the recent announcement of a project collaboration in Romania. SMRs are emerging as a new energy technology that are designed to be more compact and adaptable compared to traditional large-scale nuclear reactors. This article will explain the concept of SMRs, highlighting their benefits and safety features, and provide details on the E&C Group’s upcoming SMR project in Romania.
What is a Small Modular Reactor (SMR)?
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are nuclear reactors that are smaller in scale and capacity compared to typical large-scale nuclear reactors. According to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), small reactors have up to 300 megawatts of electric capacity (MWe) while medium sized reactors have up to 700 MWe. By comparison, typical large-scale nuclear power plants have over 1,000 MWe.
The modular design of SMRs means they can be built off-site in large numbers, reducing construction times and costs. SMRs are emerging as a low-carbon energy solution that offer lower capital investment, enhanced safety features, and grid stability.

How do Small Modular Reactors Generate Power?
SMRs create nuclear fission reactions to generate thermal energy that is then converted into electricity. Inside an SMR, the fission reactions are controlled within pressure vessels that generate heat which then produces steam and spins turbines to produce low-carbon electricity. SMRs have around one-third of the processing power of larger nuclear plants but are designed to be flexible and have advanced safety features.
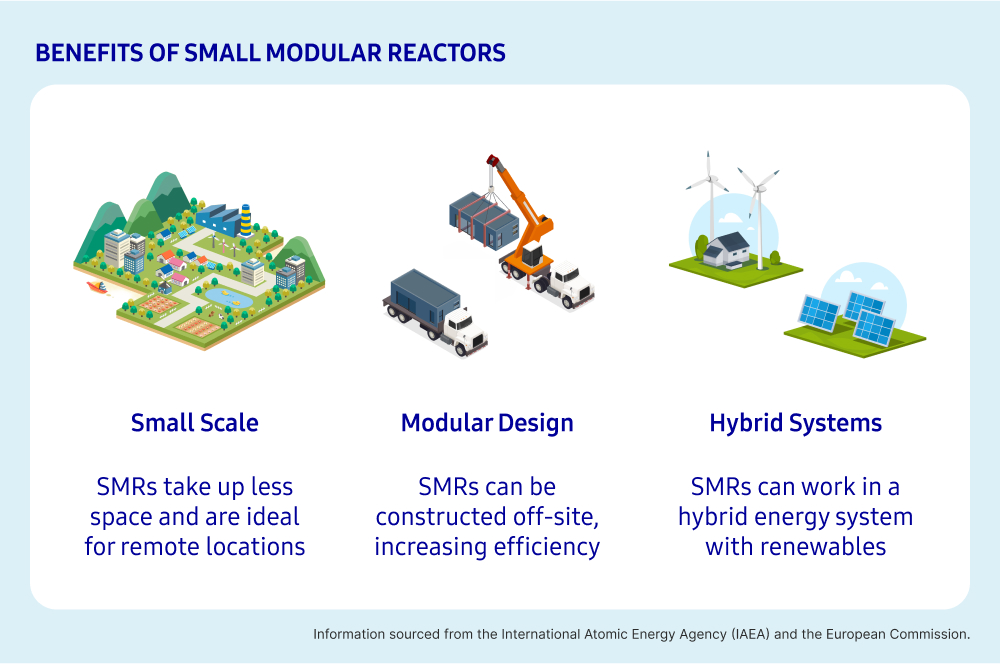
What are the benefits of Small Modular Reactors?
- Small Scale
Due to their smaller size, power output, and capacity, SMRs take up less space and require less cooling water. Their small size makes them ideal for remote geographical locations that have less access to cooling water or have less space for large power plants such as small islands.
- Modular Construction
Typical large-scale nuclear power plants generally have a complex construction process that requires large investment. The modular design of SMRs means they can be assembled in factories which enables opportunities for mass production. SMRs can be transported as modules or complete units to their sites, reducing installation time and costs.
- Hybrid Energy Systems
Renewable energy sources such as wind and solar depend on weather conditions and the time of day. When needed, SMRs can be used to bring power to homes and cities when renewable energy sources are insufficient without relying on fossil fuels.
Safety Innovations in Small Modular Reactors
- Enhanced Safety
SMRs utilize advanced safety mechanisms, including passive safety systems that can operate without human intervention in emergencies. SMRs are also built with inherent safety characteristics such as lower power outputs and operating pressures.
- Reduced Risk of Radioactivity Release
The enhanced safety features of SMRs significantly reduce the risk of unsafe releases of radioactivity, minimizing the potential for environmental damage or harm to public safety.
Powering the Future: Samsung C&T Enters the Global SMR Market
In June 2023, the Samsung C&T E&C Group signed a Memorandum of Understanding with five global nuclear power companies. This includes the Romanian Societatea Nationala Nuclearelectrica (SNN) and U.S. companies NuScale Power Corporation (hereby referred to as NuScale) and Fluor.
The Samsung C&T E&C Group also recently announced its collaboration on the front-end engineering design (FEED) of an SMR project in Romania. FEED refers to establishing preliminary plans for a project, including permits, construction time and costs, and EPC (engineering, procurement, and construction) execution.
The project in Romania involves replacing an existing coal-fired power plant with a 462 MW SMR, which is aiming for commercial operation by 2030. The SMR is based on NuScale’s technology, the only company with SMR technology approved by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC). This project is an important milestone for replacing coal-fired power plants in Europe, where the Samsung C&T E&C Group is positioning itself as a key player in the global SMR market.
Across Eastern Europe, coal-fired power plants are targeting closures by 2030, which will provide many opportunities for the E&C group to expand its SMR business.







